| Progress 20% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ancient Va'aini Quūvarānī | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | |||
| Agglutinative | |||
| Alignment | |||
| Ergative-Absolutive | |||
| Head direction | |||
| Final | |||
| Tonal | |||
| No | |||
| Declensions | |||
| No | |||
| Conjugations | |||
| No | |||
| Genders | |||
| No | |||
| Nouns decline according to... | |||
| Case | Number | ||
| Definiteness | Gender | ||
| Verbs conjugate according to... | |||
| Voice | Mood | ||
| Person | Number | ||
| Tense | Aspect | ||
General information[]
The first written language in all of Nirūnei, it was made by the Laivanī of Va'ainū and used an alphabet reminiscent of Semitic scripts, representing only consonants. It is highly agglutinative (sorry, gave up on making it polysynthetic. It's..close though), compared to more analytical languages like English, or fusional languages such as Latin or Greek.
Phonology[]
Consonants[]
| Labial | Alveolar | Post-alveolar | Velar | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m |
n |
|||
|
Plosive |
p, b | t, d |
g, gu, c, qu |
' | |
| Fricative | f, v |
s, z |
š | h | |
| Affricate |
č |
||||
| Approximant |
l |
||||
| Trill |
r |
Notice: There are much more consonants than before. This is because I have made the switch so that vowels are not written, so I needed more consonants so that words could be more distinct.
Related Consonants[]
Some consonants are very phonetically similar and were represented by the same letter in the Quūvarānī alphabet, only with a bar above to distinguish one from the other. For the most part, this is for voiced versus unvoiced, however there are a few exceptions. The alphabet chart explains which consonants are related and which is "dominant" (dominant consonants have the bar over them.)
Vowels[]
| Front | Near-front | Central | Near-back | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Close | ī | ū | |||
| Near-close | i | u | |||
| Close-mid | e | o | |||
| Mid | |||||
| Open-mid | ē | ||||
| Near-open | |||||
| Open | a/ā |
The only diphthongs are "ou" (which is the only way the letter o is ever used) "ei" and "ai." NB: the diphthong "ou" is written "ō" and pronounced as in "oh."
All vowels can be lengthened by adding a macron. For most vowels, the pronunciation changes as well as the time it is held, except for a, which is simply held longer.
Alphabet[]
| Letter | Name | Dominant Consonant | Non-Dominant Consonant |
|---|---|---|---|
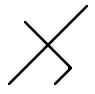 |
Malācū | m | n |
 |
Pilāgei | p | b |
 |
Taremī | t | d |
 |
Curešī | c | g |
 |
Qualeimā | qu | gu |
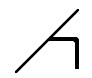 |
Falāca | f | v |
 |
Sirūlī | s | z |
 |
Čīlaquei | č | š |
 |
'arešī | ' | h |
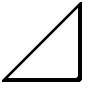 |
Lešīla | l | r |
Beneath is the entire Quūvarānī alphabet in four possible combinations: the first row features non-dominant consonants with short vowels, the second dominant consonants with short vowels, the third non-dominant with long vowels or diphthongs, and the last dominant consonants with long vowels or diphthongs. Note that though vowels are not indicated orthographically, whether or not they are long (diphthongs are considered long) is, to help with pronunciation of stress.

Phonotactics[]
Quūvarani has a very simple set of phonotactics due to its alphabet, with a strict CVCV... pattern with no method of deviation. This is helpful because of the fact that vowels were not indicated orthographically.
Grammar[]
Quūvarānī is a heavily agglutinative language, so where in English where we would use multiple prepositions, adverbs, particles and infinitives, Quūvarānī would often have a verb mood or noun case to express it in one word (especially where in English a verb often takes an infinitive, and when prepositions are used)
Cases[]
| Case | Ending | English Example | Grammatical Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Ergative |
None (default) | I hit him. | Subject of transitive verb |
| Absolutive | -qua |
I am well/ he hit me |
Subject of intransitive verb/ Direct object |
|
Dative |
-ga | I give a gift to you | Indirect object |
|
Genitive |
-nī | His dog | Possession |
|
Descriptive |
-lī |
Made of/ some of/ about |
Partitive, Quantitive |
|
Allative |
-rō | I walk to the store | Place to |
|
Pre-Proximative |
-'ōrī |
I am in front of him |
Place where in relation to |
|
Post-Proximative |
-'ōvē |
I am behind him |
Place where in relation to |
|
Proximitive |
-'ō |
I am near him |
Place where in relation to |
|
Locative |
-tō | I am at the store | Place where |
|
Ablative |
-šō |
I am walking from the store |
Place from |
Vocabulary[]
| No. | English | Quūvarānī |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | I | — |
| 2 | you (singular) | — |
| 3 | he | — |
| 4 | we | — |
| 5 | you (plural) | — |
| 6 | they | — |
| 7 | this | — |
| 8 | that | — |
| 9 | here | — |
| 10 | there | — |
| 11 | who | — |
| 12 | what | — |
| 13 | where | — |
| 14 | when | — |
| 15 | how | — |
| 16 | not | — |
| 17 | all | — |
| 18 | many | — |
| 19 | some | — |
| 20 | few | — |
| 21 | other | — |
| 22 | one | — |
| 23 | two | — |
| 24 | three | — |
| 25 | four | — |
| 26 | five | — |
| 27 | big | — |
| 28 | long | — |
| 29 | wide | — |
| 30 | thick | — |
| 31 | heavy | — |
| 32 | small | — |
| 33 | short | — |
| 34 | narrow | — |
| 35 | thin | — |
| 36 | woman | — |
| 37 | man (adult male) | — |
| 38 | man (human being) | — |
| 39 | child | — |
| 40 | wife | — |
| 41 | husband | — |
| 42 | mother | — |
| 43 | father | — |
| 44 | animal | — |
| 45 | fish | — |
| 46 | bird | — |
| 47 | dog | — |
| 48 | louse | — |
| 49 | snake | — |
| 50 | worm | — |
| 51 | tree | — |
| 52 | forest | — |
| 53 | stick | — |
| 54 | fruit | — |
| 55 | seed | — |
| 56 | leaf | — |
| 57 | root | — |
| 58 | bark | — |
| 59 | flower | — |
| 60 | grass | — |
| 61 | rope | — |
| 62 | skin | — |
| 63 | meat | — |
| 64 | blood | — |
| 65 | bone | — |
| 66 | fat | — |
| 67 | egg | — |
| 68 | horn | — |
| 69 | tail | — |
| 70 | feather | — |
| 71 | hair | — |
| 72 | head | — |
| 73 | ear | — |
| 74 | eye | — |
| 75 | nose | — |
| 76 | mouth | — |
| 77 | tooth | — |
| 78 | tongue | — |
| 79 | fingernail | — |
| 80 | foot | — |
| 81 | leg | — |
| 82 | knee | — |
| 83 | hand | — |
| 84 | wing | — |
| 85 | belly | — |
| 86 | guts | — |
| 87 | neck | — |
| 88 | back | — |
| 89 | breast | — |
| 90 | heart | — |
| 91 | liver | — |
| 92 | drink | — |
| 93 | eat | — |
| 94 | bite | — |
| 95 | suck | — |
| 96 | spit | — |
| 97 | vomit | — |
| 98 | blow | — |
| 99 | breathe | — |
| 100 | laugh | — |
| 101 | see | — |
| 102 | hear | — |
| 103 | know | — |
| 104 | think | — |
| 105 | smell | — |
| 106 | fear | — |
| 107 | sleep | — |
| 108 | live | — |
| 109 | die | — |
| 110 | kill | — |
| 111 | fight | — |
| 112 | hunt | — |
| 113 | hit | — |
| 114 | cut | — |
| 115 | split | — |
| 116 | stab | — |
| 117 | scratch | — |
| 118 | dig | — |
| 119 | swim | — |
| 120 | fly | — |
| 121 | walk | — |
| 122 | come | — |
| 123 | lie | — |
| 124 | sit | — |
| 125 | stand | — |
| 126 | turn | — |
| 127 | fall | — |
| 128 | give | — |
| 129 | hold | — |
| 130 | squeeze | — |
| 131 | rub | — |
| 132 | wash | — |
| 133 | wipe | — |
| 134 | pull | — |
| 135 | push | — |
| 136 | throw | — |
| 137 | tie | — |
| 138 | sew | — |
| 139 | count | — |
| 140 | say | — |
| 141 | sing | — |
| 142 | play | — |
| 143 | float | — |
| 144 | flow | — |
| 145 | freeze | — |
| 146 | swell | — |
| 147 | sun | — |
| 148 | moon | — |
| 149 | star | — |
| 150 | water | — |
| 151 | rain | — |
| 152 | river | — |
| 153 | lake | — |
| 154 | sea | — |
| 155 | salt | — |
| 156 | stone | — |
| 157 | sand | — |
| 158 | dust | — |
| 159 | earth | Cālōcī (earth) Nirūnei (planet) |
| 160 | cloud | — |
| 161 | fog | — |
| 162 | sky | — |
| 163 | wind | — |
| 164 | snow | — |
| 165 | ice | — |
| 166 | smoke | — |
| 167 | fire | — |
| 168 | ash | — |
| 169 | burn | — |
| 170 | road | — |
| 171 | mountain | — |
| 172 | red | — |
| 173 | green | — |
| 174 | yellow | — |
| 175 | white | — |
| 176 | black | — |
| 177 | night | — |
| 178 | day | — |
| 179 | year | — |
| 180 | warm | — |
| 181 | cold | — |
| 182 | full | — |
| 183 | new | — |
| 184 | old | — |
| 185 | good | — |
| 186 | bad | — |
| 187 | rotten | — |
| 188 | dirty | — |
| 189 | straight | — |
| 190 | round | — |
| 191 | sharp | — |
| 192 | dull | — |
| 193 | smooth | — |
| 194 | wet | — |
| 195 | dry | — |
| 196 | correct | — |
| 197 | near | — |
| 198 | far | — |
| 199 | right | — |
| 200 | left | — |
| 201 | at | — |
| 202 | in | — |
| 203 | with | — |
| 204 | and | — |
| 205 | if | — |
| 206 | because | — |
| 207 | name | — |
